Discover the comprehensive guide on what muscles does swimming exercise. Swimming isn’t just a leisurely activity; it’s a full-body workout that engages various muscle groups while providing a host of health benefits. Whether you’re doing laps in the pool or enjoying a swim in the open water, the effects on your body are undeniable.
Importance of Swimming for Fitness
Swimming stands out as an exceptional form of exercise due to its multifaceted benefits. It serves as a powerful cardiovascular workout, elevating the heart rate and improving circulation. Moreover, it offers a comprehensive full-body workout, toning muscles from head to toe. Despite its effectiveness, swimming is gentle on the joints, making it an ideal choice for individuals with joint issues or those recovering from injuries. Additionally, swimming has profound mental health benefits, promoting relaxation and reducing stress levels.

What Muscles Does Swimming Exercise?
Swimming targets a wide array of muscle groups, making it one of the most comprehensive workouts available.
Overview of Muscle Groups Involved
In essence, swimming engages nearly all major muscle groups in the body. From the arms and shoulders to the core, back, and legs, each stroke involves coordinated effort from multiple muscles.
Swimmer’s muscle name
The swimmer’s muscle, also known as the latissimus dorsi, is a powerful and broad muscle located on the back. Its name derives from its common usage and development among swimmers due to the stroke mechanics involved in swimming, where it plays a significant role in propelling the body forward during strokes like the crawl and butterfly. The latissimus dorsi extends from the lower spine to the upper arm, contributing to various movements such as pulling, lifting, and rotating the arms. Its well-defined shape and function make it a key muscle for swimmers seeking to enhance their performance in the water.
The latissimus dorsi is not only crucial for swimming but also for a range of other activities involving upper body movement, such as rowing, climbing, and lifting. Its large size and location make it one of the primary muscles responsible for creating a strong and stable core. Regular training of the latissimus dorsi can improve overall upper body strength and endurance, aiding in the prevention of injuries and enhancing athletic performance across various sports and activities. Additionally, its development contributes to a well-balanced physique, making it a focal point in many strength-training regimens.
Primary Muscles Targeted
The primary muscles engaged during swimming vary depending on the stroke used. For instance, the freestyle stroke primarily targets the muscles of the upper body, including the deltoids, latissimus dorsi, and trapezius muscles. Meanwhile, the breaststroke places emphasis on the chest, quadriceps, and inner thighs.
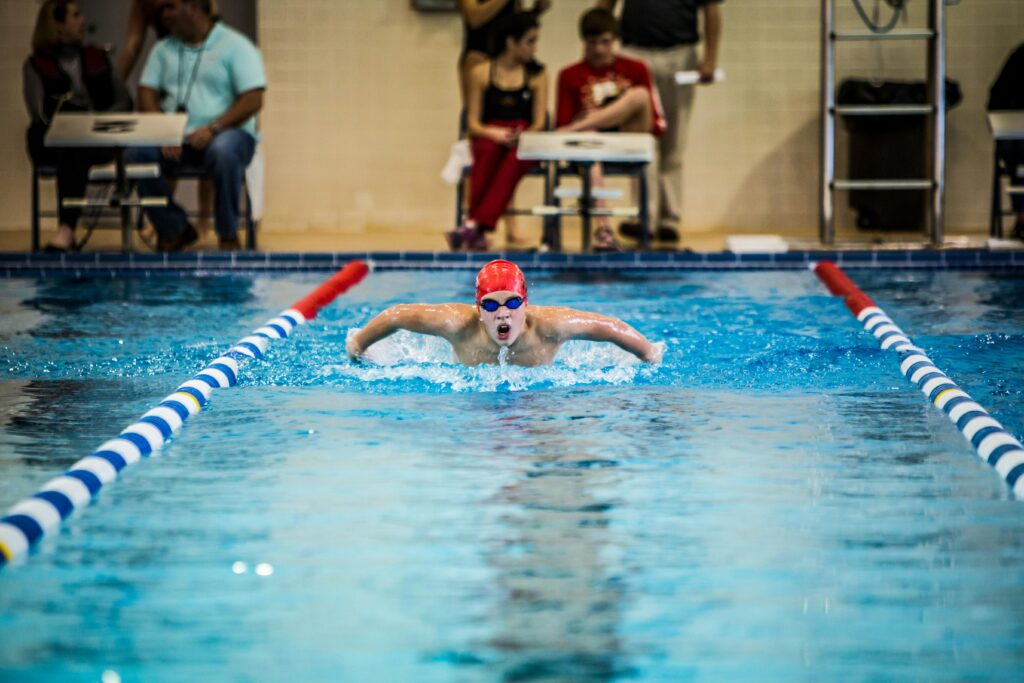
Secondary Muscles Engaged
While certain muscles take the lead, many others play a supportive role. For example, the core muscles, including the abdominals and obliques, act as stabilisers, maintaining proper body position and balance throughout the swim. Similarly, the glutes and hamstrings contribute to propulsion and overall lower body strength.
Impact on Core Muscles
Swimming is particularly effective at strengthening the core muscles, which are essential for stability and balance. Each stroke requires core engagement to maintain proper body alignment and streamline movement through the water.
Comparison with Other Exercises
Unlike some forms of exercise that target specific muscle groups, swimming provides a comprehensive full-body workout. While activities like weightlifting or running may focus on isolated muscle groups, swimming engages multiple muscles simultaneously, resulting in a more balanced and functional form of fitness.
Techniques for Effective Muscle Engagement
To maximize the muscle-building benefits of swimming, it’s essential to focus on proper technique and form.
Proper Stroke Techniques
Each swimming stroke has its own unique set of techniques and movements. Learning the correct form for strokes such as freestyle, backstroke, breaststroke, and butterfly ensures optimal muscle engagement and efficiency in the water.
Breathing Techniques
Effective breathing is crucial for endurance and performance in swimming. Practising rhythmic breathing patterns and mastering the art of bilateral breathing enhances oxygen intake and overall stamina during workouts.
Focus on Form and Efficiency
Efficient swimming relies on streamlined body position and minimal drag in the water. By refining stroke technique and minimising wasted movements, swimmers can maximise the effectiveness of their workouts and reduce the risk of injury.
Variation in Swimming Styles
Incorporating a variety of swimming styles and drills into your routine challenges different muscle groups and prevents monotony. Whether it’s interval training, kicking drills, or using swimming aids like pull buoys and paddles, mixing up your workouts keeps muscles engaged and promotes continuous improvement.
Incorporating Resistance Training
In addition to traditional swimming workouts, incorporating resistance training exercises can further enhance muscle strength and endurance. Using equipment such as resistance bands or performing bodyweight exercises in the water adds an extra layer of challenge and variety to your routine.
Swimming Muscles Before And After
Swimming relies on a multitude of muscles, and the specific muscles engaged can vary depending on the stroke being used. Before engaging in regular swimming, the muscles involved may lack definition and strength, particularly in the shoulders, arms, core, and legs. However, with consistent swimming practice, these muscles undergo significant development.
The shoulders and arms, crucial for propelling through the water, become more defined and stronger, while the core muscles improve stability and streamline in the water. Additionally, the leg muscles, often overlooked, also experience enhancement, providing better propulsion and endurance. Overall, regular swimming leads to a noticeable transformation in muscle tone, strength, and endurance, making it an excellent full-body workout for individuals of all fitness levels.
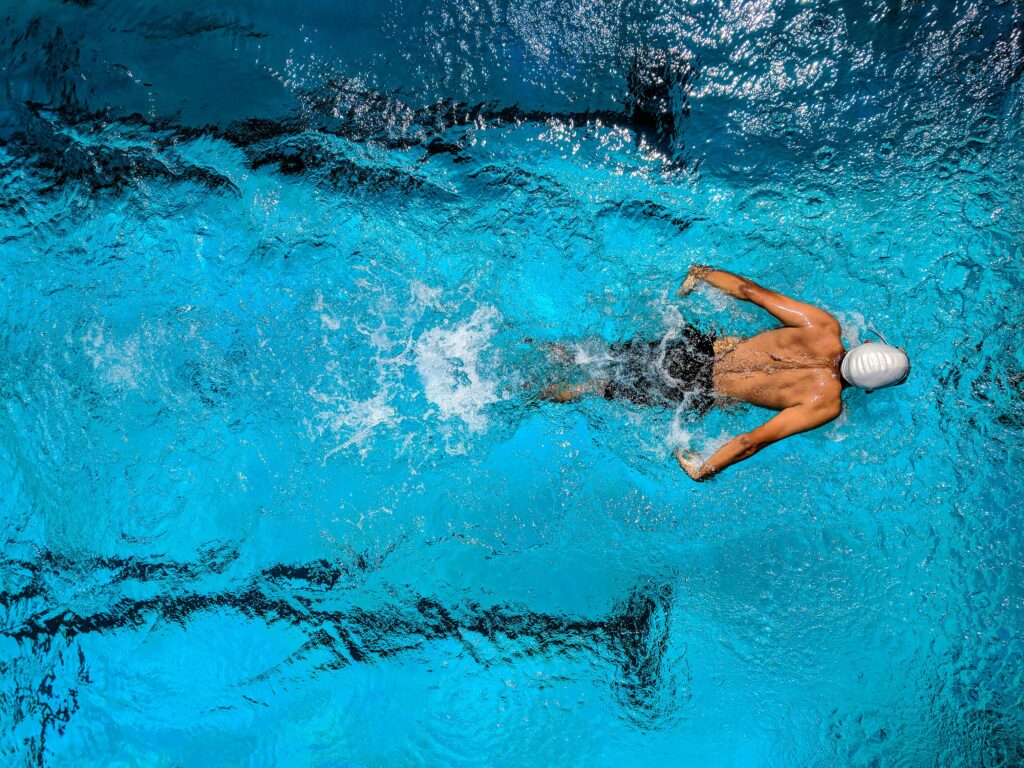

Muscles used in swimming and front crawl
Swimming front crawl, commonly known as freestyle, engages a multitude of muscles throughout the body to propel the swimmer forward efficiently. The primary muscles involved in front crawling include those of the upper body, such as the latissimus dorsi, pectoralis major, deltoids, and triceps, which work together to pull the arms through the water.
Additionally, the muscles of the core, including the rectus abdominis, obliques, and erector spine, provide stability and support, aiding in the generation of power and maintaining proper body alignment. Furthermore, the kicking motion in the front crawl heavily relies on the quadriceps, hamstrings, glutes, and calf muscles to produce the necessary force to propel the body forward. Coordination between these muscle groups allows for a smooth and efficient swimming stroke, making front crawling a demanding yet rewarding full-body workout.
Frequently Asked Questions: What Muscles Does Swimming Exercise?
- Does swimming build muscle? Swimming is an excellent way to build lean muscle mass, especially in the upper body, core, and legs. However, it may not result in significant muscle hypertrophy, like weightlifting.
- How often should I swim to see results? Consistency is key when it comes to seeing results from swimming. Aim for at least three to four sessions per week to experience improvements in strength, endurance, and overall fitness.
- Can swimming help with weight loss? Yes, swimming can aid in weight loss by burning calories and increasing metabolic rate. However, it’s essential to pair swimming with a balanced diet and other forms of exercise for optimal results.
- Is swimming a good workout for seniors? Absolutely! Swimming is an ideal form of exercise for seniors due to its low-impact nature and the ability to customise intensity levels. It’s gentle on the joints while providing a thorough workout for the entire body.
- How does swimming benefit mental health? Swimming promotes relaxation and reduces stress levels by encouraging rhythmic breathing and providing a sense of weightlessness in the water. It’s also an opportunity for mindfulness and meditation.
- Can swimming improve flexibility? Yes, swimming can improve flexibility by increasing range of motion in the joints and stretching muscles throughout the body. Regular swimming sessions can lead to greater flexibility over time.
Conclusion
In conclusion, swimming is a powerhouse of exercise, offering a multitude of physical and mental health benefits. By engaging numerous muscle groups and providing a low-impact, full-body workout, swimming stands out as a versatile and effective form of fitness for individuals of all ages and fitness levels. So, dive in, reap the rewards, and let the water work its magic on your mind and body.

I am a health writer and blogger based in the US and UK. I have been with the health department for six years. And I give advice on various health problems and solutions. I have a lot of experience in health matters and I share it here.

