Find out what joint do you use to lift weight. Enhance your fitness regimen by learning about joint involvement in strength training. The joint used to lift weight is the elbow. It is essential for bending and straightening the arm to lift objects.
When engaging in weightlifting, knowing the proper joint mechanics is crucial for preventing injuries and maximizing strength gains. Weightlifting involves a variety of joints and muscles working together to perform movements. Proper form, including the use of the elbow joint, is crucial for effective and safe weightlifting.
Understanding how the elbow joint functions and the role it plays in lifting weights can help individuals optimize their workouts and minimize the risk of injury. We will explore the importance of the elbow joint in weightlifting and provide tips for incorporating it into your routine for better results.
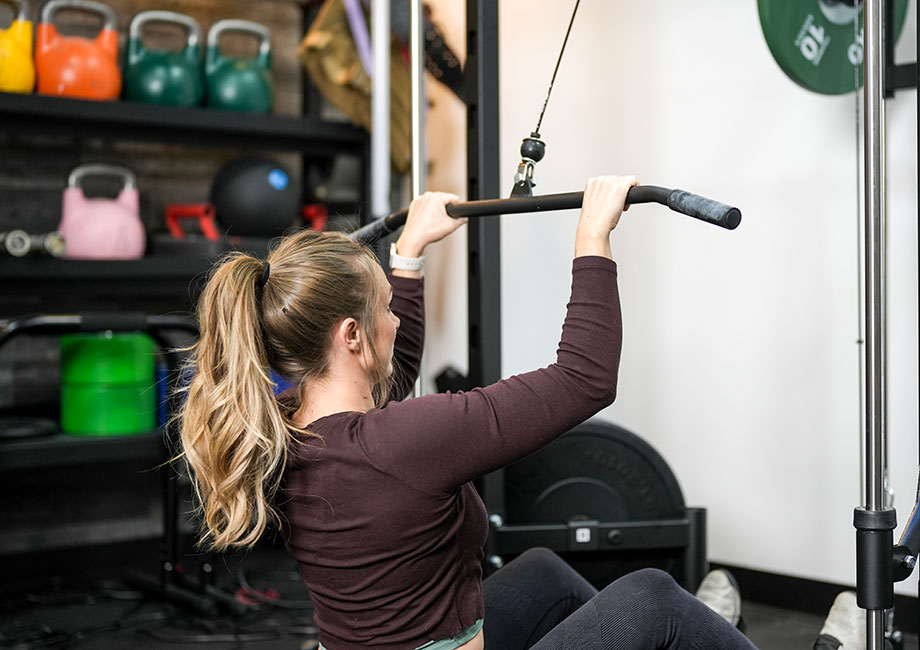
The Role Of The Shoulders
The shoulder joint plays a key role in lifting weights, providing mobility and stability. It consists of tendons, ligaments, and muscles that work together to facilitate movement. When lifting, the shoulders play a crucial role in ensuring proper form and stability, thereby reducing the risk of injury.
Anatomy Of The Shoulder Joint
The human shoulder joint, also known as the glenohumeral joint, is one of the most mobile joints in the body. It permits flexion, extension, abduction, adduction, rotation, and circumduction, among other extensive range of motions.
- Glenoid Cavity: This is a shallow socket on the scapula (shoulder blade) that receives the humeral head (upper arm bone).
- Humerus: The upper arm bone, or humerus, forms the ball-shaped component of the shoulder joint.
- Rotator Cuff Muscles: The rotator cuff is comprised of four muscles that surround the shoulder joint, providing stability and helping with movement.
- Ligaments: Ligaments are bands of connective tissue that connect bone to bone, helping to reinforce the joint and prevent excessive movement.
- Tendons: Tendons connect muscles to bones, allowing for the transfer of force from the muscles to the bones during movement.
- Labrum: The labrum is a ring of cartilage that lines the glenoid cavity, providing additional stability to the shoulder joint.
Proper Form For Shoulder Exercises
When it comes to shoulder exercises, proper form is crucial to prevent injuries and maximize the effectiveness of your workout. Here are a few tips to ensure that you maintain proper form during shoulder exercises:
- Warm-up: Before starting any shoulder exercises, warm up your shoulder joint by performing light cardio or dynamic stretching to increase the blood flow and range of motion in the muscles and joints.
- Maintain Good Posture: During shoulder exercises, maintain a straight spine, engage your core, and avoid excessive arching or rounding of the back.
- Start with Light Weights: If you’re new to shoulder exercises or returning from an injury, start with light weights and gradually increase the load as your strength and endurance improve.
- Avoid Overhead Lifting: If you have a pre-existing shoulder injury or limited mobility, avoid exercises that involve lifting weights directly overhead, as this can put excessive strain on the shoulder joint.
- Focus on Controlled Movements: Rather than rushing through the exercises, focus on controlled movements and proper form to target the muscles effectively and reduce the risk of injury.
- Listen to Your Body: Pay attention to any pain or discomfort during shoulder exercises. Exercise should be stopped and medical advice should be sought if you feel severe or ongoing pain.
By following these guidelines, you can ensure that your shoulder exercises are safe, effective, and contribute to your overall fitness goals. Remember to always prioritize proper form and consult with a qualified fitness professional if you have any concerns or specific medical conditions.

Credit: www.garagegymreviews.com
The Importance Of The Hips
Lifting weights involves various joints and muscles, but one of the most crucial joints when it comes to weightlifting is the hip joint. The hips play a significant role in providing stability and power when lifting, making them vital in ensuring proper form and maximizing strength. Understanding the anatomy of the hip joint and incorporating effective hip exercises into your routine can greatly enhance your weightlifting performance.
Anatomy Of The Hip Joint
The hip joint is a ball-and-socket joint, formed by the articulation between the femur and the acetabulum of the pelvis. This anatomical structure allows for a wide range of motion, facilitating movements such as hip flexion, extension, abduction, adduction, and rotation. The joint is supported by a network of muscles, ligaments, and tendons that work together to provide stability and mobility during weightlifting activities.
Effective Hip Exercises
- Squats: This compound movement engages the hips, targeting the glutes and quadriceps, to develop strength and power.
- Deadlifts: By hinging at the hips, deadlifts activate the posterior chain and stimulate hip extension, contributing to overall lifting strength.
- Hip Thrusts: Specifically designed to target the glutes, hip thrusts improve hip extension and enhance lower body explosiveness.
These hip exercises not only strengthen the muscles around the hip joint but also help improve hip mobility and stability. Incorporating these movements into your workout routine can lead to enhanced weightlifting performance and reduced risk of injury.
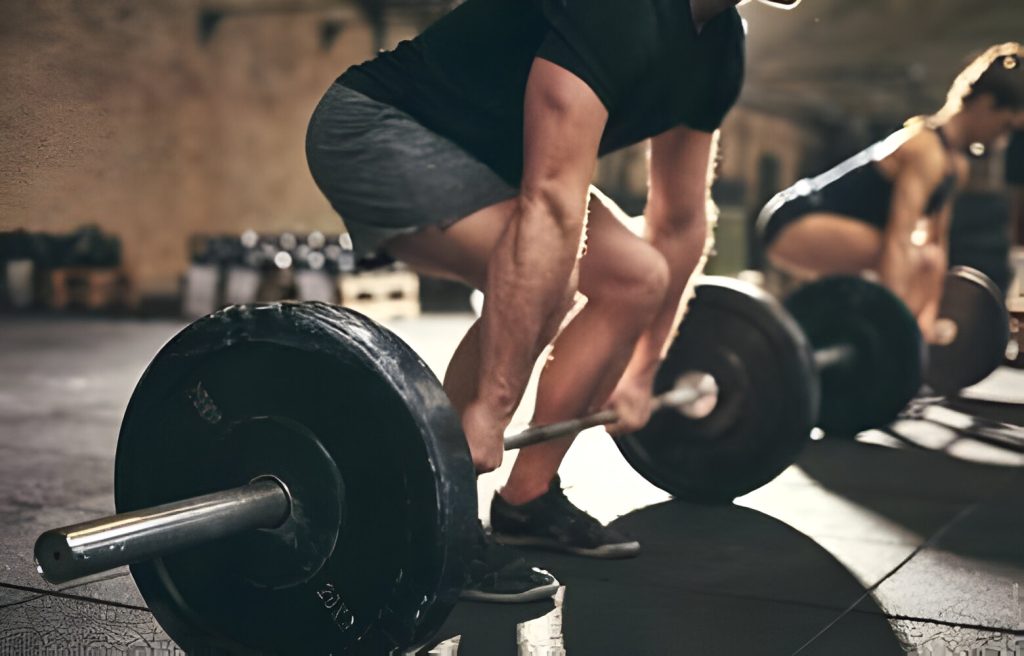
The Strength Of The Knees
Your knees play a crucial role in weightlifting, providing the foundation and stability necessary for proper form and lifting technique. Understanding the anatomy of the knee joint is key to safeguarding them during weightlifting activities.
Anatomy Of The Knee Joint
The knee joint is composed of bones, ligaments, tendons, and cartilage that work together to support and facilitate movement. The main parts of the knee joint include the femur, tibia, patella, and various ligaments like the ACL and PCL.
Protecting Your Knees During Weightlifting
- Proper Form: Maintain a stable stance and avoid locking your knees to prevent unnecessary strain.
- Warm-up: Engage in dynamic stretches and warm-up exercises to increase blood flow and flexibility in the knee joint.
- Gradual Progression: Increase weight gradually to allow your knees to adapt and strengthen over time.

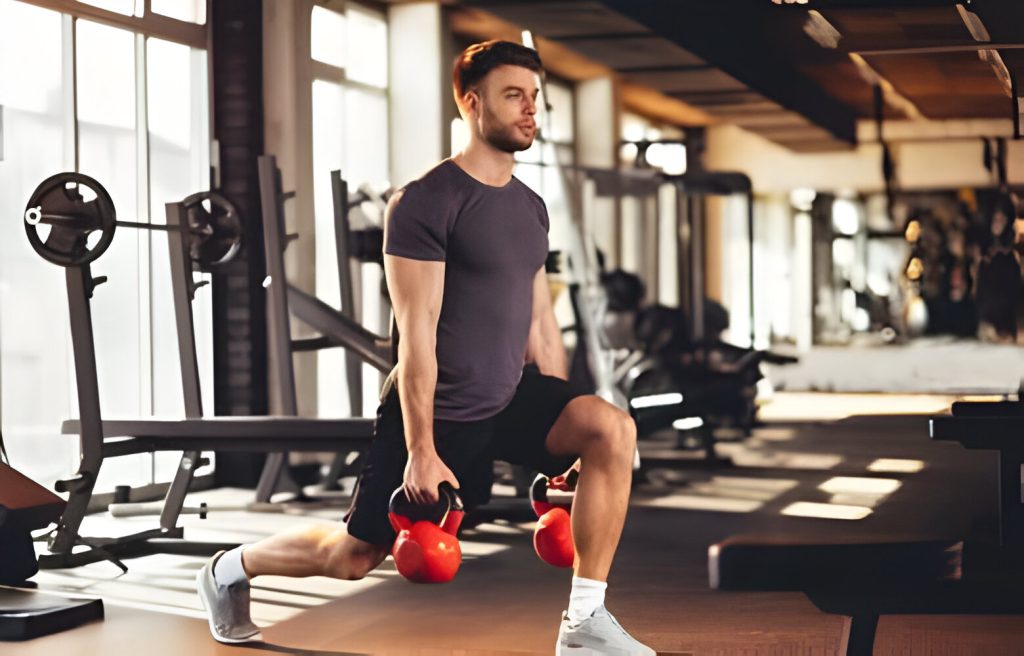
The Power Of The Elbows
When it comes to weightlifting, it’s important to understand the role of different joints in executing exercises and maintaining proper form. One joint that often gets overlooked but plays a crucial role in many lifts is the elbow joint. The elbows are a powerhouse when it comes to weightlifting, providing stability, control, and strength. Let’s dive into the anatomy of the elbow joint and explore how to prevent common elbow injuries.
Anatomy Of The Elbow Joint
The elbow joint is a hinge joint formed by the articulation of three bones: the humerus, radius, and ulna. These bones are held together by ligaments and supported by muscles, tendons, and cartilage. Flexion and extension are the primary movements that the elbow joint allows, allowing us to bend and straighten our elbows. The joint also permits some rotation, such as during forearm movements.
To paint a clear picture, here’s a breakdown of the bones and structures involved in the elbow joint:
| Bone | Structure |
|---|---|
| Humerus | The upper arm bone and the largest bone of the elbow joint. It connects the shoulder and the lower arm. |
| Radius | A forearm bone on the thumb side of the elbow joint. It supports the muscles involved in wrist and thumb movements. |
| Ulna | The other forearm bone is on the pinky side of the elbow joint. It provides stability and supports the muscles for gripping and rotating motions. |
| Ligaments | Connective tissues that hold the bones of the elbow joint together, providing stability and preventing excessive movement. |
| Muscles and tendons | These structures work together to move the elbow, extend and flex the forearm, and rotate the wrist. |
| Cartilage | Smooth, rubbery tissue that covers the ends of the bones, reducing friction and allowing smooth movements within the joint. |
Preventing Elbow Injuries
Given the importance of the elbows in weightlifting, it’s crucial to take preventive measures to avoid common elbow injuries. Here are some tips to keep your elbows healthy and strong:
- Warm-up: Prioritize a thorough warm-up routine before every weightlifting session. This can include gentle range-of-motion exercises and dynamic movements to increase blood flow and prepare the elbows for exercise.
- Proper technique: Ensure you maintain proper form and technique throughout your lifts. Avoid overextending the elbow joint, as this can put excessive stress on the structures and increase the risk of injury.
- Progression: Gradually increase the weight and intensity of your lifts to allow your elbows time to adapt and strengthen. Sudden jumps in load can place unnecessary strain on the joint.
- Strengthen supporting muscles: Focus on strengthening the muscles surrounding the elbow joint, such as the biceps and triceps. This helps to stabilize the joint and reduce the risk of injury.
- Rest and recovery: Allow sufficient rest days between weightlifting sessions to give your body, including your elbows, time to recover and repair. Adequate sleep and nutrition also play a vital role in maintaining joint health.
By understanding the anatomy of the elbow joint and implementing these preventive measures, you can avoid common elbow injuries and optimize your performance during weightlifting sessions. Don’t neglect the power of your elbows in supporting your lifts and achieving your fitness goals.

Maintaining Healthy Joints
To lift weights effectively and maintain healthy joints, engage the shoulder and elbow joints. Proper form is crucial to prevent injuries and promote joint stability during weightlifting sessions. Strengthening these joints through targeted exercises can enhance overall performance and reduce the risk of strain or discomfort.
Strengthening Exercises For Joints
One of the best ways to maintain healthy joints is through regular strengthening exercises. These exercises help to strengthen the muscles around the joints, providing support and stability. These are some efficient workouts that you can include in your regimen:
- Squats: Stand with your feet shoulder-width apart, then slowly lower your body as if sitting back into a chair. Maintain your knees behind your toes and your weight on your heels. Repeat after getting back up to your feet.
- Lunges: Step forward with one foot and bend both knees to a 90-degree angle with your body. Return to a standing position by pushing through your front heel, and then switch to the opposite leg.
- Plank: Get into a push-up position, resting on your forearms instead of your hands. Maintaining your body in a straight line, contract your core muscles. Hold for 30 seconds to 1 minute, or as long as you can maintain proper form.
- Bridge: With your knees bent and your feet flat on the ground, lie on your back. Elevate your hips from the floor until your torso creates a straight line connecting your shoulders and knees. At the peak, pause, descend again, and repeat.
- Leg Press: Using a leg press machine or resistance band, push against the weight or band with your legs until they are fully extended. Retrace your steps slowly to the beginning and do it again.
Proper Warm-up And Stretching
In addition to strengthening exercises, it is crucial to incorporate proper warm-up and stretching techniques into your fitness routine. These activities help to prepare the joints for physical activity and improve flexibility, reducing the risk of injury. Here are some tips for a proper warm-up and stretching:
- Cardiovascular Warm-up: Start with a few minutes of light cardio exercise, such as jogging, cycling, or jumping jacks, to increase your heart rate and warm up your body.
- Dynamic Stretching: Perform dynamic stretches that involve movement, such as leg swings, arm circles, and walking lunges. This helps to improve range of motion and flexibility in the joints.
- Static Stretching: After your workout, include static stretches that involve holding a stretch for around 15-30 seconds. Focus on major muscle groups like calves, hamstrings, quads, and shoulders.
By incorporating these strengthening exercises, warm-up, and stretching techniques into your fitness routine, you can maintain healthy and strong joints. Always pay attention to your body’s signals, begin carefully, and progressively increase the duration and intensity of your workouts.

Credit: drmanalyounis.com
Frequently Asked Questions Of What Joint Do You Use To Lift Weight
Which Joint Did You Use To Lift The Weight?
I used my shoulder joint to lift the weight.
What Joint Did You Use To Lift The Weight Quizlet?
You use the hinge joint to lift weights, according to Quizlet. One direction of movement is possible with this joint.
Which Joint Is Used When A Person Lifts Weights To Build Up His Biceps?
The elbow joint is used when lifting weights to build up the biceps.
Which Muscles Contracted As You Raised The Weight?
The muscles that contract when you raise the weight are primarily the biceps, deltoids, and trapezius.
Conclusion
Understanding which joint to use when lifting weights is crucial for preventing injuries and maximizing your workout. By focusing on proper form and engaging the correct joints, you can achieve better results while safeguarding your body. Incorporating this knowledge into your training routine will undoubtedly enhance your overall fitness experience.

I am a health writer and blogger based in the US and UK. I have been with the health department for six years. And I give advice on various health problems and solutions. I have a lot of experience in health matters and I share it here.