To read nutrition labels, look for serving size and calories per serving, then check the percent daily value for key nutrients. Nutrition labels provide important information about the nutritional content of food products.
Understanding these labels can help you make informed decisions about your diet and overall health. The first step in reading a nutrition label is to check the serving size and the number of servings per container. This will help you determine how much of the food you are actually consuming.
Next, look at the calories per serving and compare it to your daily calorie needs. It is also important to pay attention to the percent daily value (%DV) for key nutrients such as fat, sodium, and sugar. This information can give you an idea of how the food fits into your overall diet. You can take charge of your nutrition and make better decisions by reading nutrition labels.
Decoding Nutrition Labels
Reading nutrition labels is an essential skill for making informed food choices. However, deciphering the information presented on these labels can feel overwhelming at times. In this guide, we will break down the key elements of nutrition labels, making it easier for you to understand and utilize the information they provide.
Serving Size And Servings Per Container
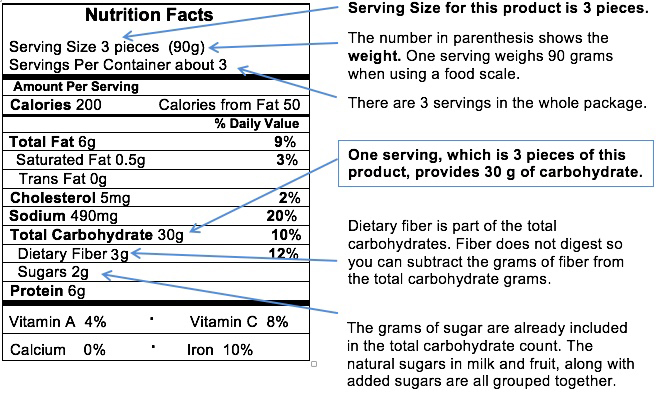
The serving size and servings per container sections of a nutrition label indicate the recommended portion size of the product.
The serving size represents the amount of food typically consumed per serving, measured in familiar units such as cups, teaspoons, or pieces. It is important to note that the serving size may not reflect the portion you typically eat, so pay attention to this information when assessing the nutritional value of a product.
The servings per container informs you how many servings are in the entire package. This is useful for understanding the total amount of nutrients and calories you will consume if you eat the entire product.
Calories And Nutrient Information
Next, let’s explore the calorie and nutrient information section.
Calories indicate the amount of energy provided by one serving of the product. This number is important to consider if you are trying to maintain or achieve a certain calorie intake. It is a key factor in managing weight and can help you make choices that align with your health goals.
The nutrient information presented on the label includes a breakdown of essential nutrients such as carbohydrates, fats, proteins, vitamins, and minerals, among others. It is usually listed as a percentage of the recommended daily intake (RDI) based on a 2,000-calorie diet. These values allow you to assess how the product contributes to your overall nutrient needs.
Remember, it is vital to pay attention to serving sizes and servings per container as you calculate your overall intake of calories and nutrients.
By familiarizing yourself with these fundamental aspects of nutrition labels, you will be equipped to make well-informed choices about the food you consume.

Credit: www.healthline.com
Understanding Daily Values
Daily Values form an important part of a nutrition label, providing key information about the nutrients in a serving of food.
Why Daily Values Matter
Daily Values are based on a 2,000 calorie diet and signify the percentage of each nutrient in one serving of the food.
Interpreting Percent Daily Value
The Percent Daily Value (%DV) helps you determine if a food is high or low in a specific nutrient.
Uncovering Hidden Ingredients
Uncovering Hidden Ingredients:
When reading nutrition labels, it’s crucial to uncover hidden ingredients that may not be obvious at first glance.
Identifying Added Sugars
Added sugars can be disguised under various names, such as sucrose, high fructose syrup, or dextrose.
Spotting Artificial Additives
Artificial additives like colorings, preservatives, and flavor enhancers are commonly hidden in processed foods.
Healthy Vs. Unhealthy Fats
Healthy fats, such as monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats, can be found in foods like avocados, nuts, and olive oil. On the other hand, unhealthy fats like trans fats and saturated fats are commonly found in processed and fried foods. When reading nutrition labels, look for products low in saturated and trans fats to make healthier choices.
Differentiating Between Fats
Understanding the difference between healthy and unhealthy fats is crucial when it comes to making informed choices about our diet. Fats are an essential part of a balanced diet, providing energy and aiding in the absorption of vitamins. However, not all fats are created equal, and it’s important to know how to read nutrition labels to distinguish between them.
When looking at nutrition labels, keep an eye out for the types of fats listed. Some common types include saturated fats, trans fats, monounsaturated fats, and polyunsaturated fats. Each type of fat has a different impact on our health, so let’s break them down:
- Saturated Fats: These fats are frequently found in animal products like meat and dairy, and they are normally solid at room temperature. They have been associated with an increased risk of heart disease when consumed in excess.
- Trans Fats: These fats are artificially created through a process called hydrogenation, which transforms liquid oils into solid fats. Trans fats are commonly found in processed foods and have been shown to contribute to heart disease and inflammation.
- Monounsaturated Fats: These fats are liquid at room temperature and can be found in foods like olive oil, avocados, and nuts. Consuming monounsaturated fats in moderation has been associated with a reduced risk of heart disease.
- Polyunsaturated Fats: Like monounsaturated fats, polyunsaturated fats are also liquid at room temperature. They are found in foods like fatty fish, walnuts, and flaxseeds and are rich in essential omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids, which play a vital role in brain function and heart health.
Impact On Heart Health
Now that we have differentiated between the different types of fats, let’s discuss their impact on heart health. Consuming excessive amounts of saturated and trans fats has been linked to an increased risk of heart disease. These fats can raise levels of harmful LDL cholesterol in the blood, contributing to the formation of plaque in the arteries.
On the other hand, replacing saturated and trans fats with healthier options, such as monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats, can have a positive impact on heart health. These fats have been shown to lower LDL cholesterol levels, reduce inflammation, and improve overall cardiovascular health.
When reading nutrition labels, it’s important to pay attention to the amount and type of fats present in the food or beverage. Opt for products that are lower in saturated and trans fats and higher in monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats. Additionally, keep an eye on the total fat content, as fats are high in calories and excessive consumption can contribute to weight gain and other health issues.
Deciphering Protein Content
When it comes to decoding nutrition labels, understanding the protein content is crucial for making informed choices about your diet. Proteins are essential for building and repairing tissues, producing enzymes and hormones, and supporting overall health. Here, we’ll explore the key factors in deciphering protein content on nutrition labels.
Complete And Incomplete Proteins
Proteins are made up of amino acids, which are often categorized as either essential or non-essential. Complete proteins contain all essential amino acids in adequate amounts and are commonly found in animal products, such as meat, fish, and dairy. In contrast, incomplete proteins lack one or more essential amino acids and are usually present in plant-based sources, such as beans, grains, and nuts.
Protein Quality And Quantity
Quality and quantity are pivotal when evaluating protein content. High-quality proteins provide all essential amino acids in the right proportions, promoting optimal health. When assessing protein quantity, aim to consume enough to meet your body’s needs. The recommended dietary allowance (RDA) for protein varies based on age, sex, and activity levels.
Cracking The Code On Carbohydrates
Understanding the role of carbohydrates in your diet is crucial for making informed choices. Nutrition labels can be overwhelming, but by focusing on key elements such as simple vs. complex carbs, fiber, and sugar content, you can gain clarity on the nutritional value of the foods you consume.
Simple Vs. Complex Carbs
When scanning nutrition labels, pay attention to the total carbohydrate content. Simple carbohydrates are quickly digested and can cause fluctuations in blood sugar levels, while complex carbohydrates take longer to break down, providing sustained energy. Look for foods high in fiber, as they often contain complex carbs, like whole grains, fruits, and vegetables.
Fiber And Sugar Content
Fiber is essential for maintaining digestive health and controlling blood sugar levels. High-fiber foods can help you feel fuller for longer periods. On the other hand, it’s important to keep an eye on sugar content. Opt for foods with minimal added sugars and focus on natural sources of sweetness, such as fruits.
Navigating Sodium And Salt Content
When it comes to maintaining a healthy diet, understanding how to read nutrition labels is essential. One important aspect of nutrition labels to pay attention to is the sodium and salt content. Excessive sodium intake can have negative health implications, so it’s crucial to navigate this information properly. In this section, we will explore the health implications of high sodium, as well as how to identify hidden sources of sodium.
Health Implications Of High Sodium
Consuming too much sodium can lead to several health issues. High sodium intake has been linked to increased blood pressure, which can put strain on the heart and increase the risk of heart disease. It can also contribute to water retention and result in bloating and discomfort. Additionally, excessive sodium consumption may lead to kidney problems, as the kidneys have to work harder to filter out the excess sodium from the body.
Identifying Hidden Sodium Sources
Sodium can sometimes be hidden in foods that we may not expect, making it important to carefully read nutrition labels. Here are some common examples of hidden sources of sodium:
- Packaged snacks and processed foods, which often contain high amounts of sodium for flavor and preservation purposes.
- Canned foods, such as soups and vegetables, as the canning process often involves adding sodium to enhance taste and extend shelf life.
- Condiments, including sauces, dressings, and marinades, which can be high in sodium, enhance flavor.
- Baked goods, like bread and pastries, may contain sodium in the form of baking soda or baking powder.
By being aware of these hidden sources, you can make more informed choices and reduce your sodium intake.
Credit: dtc.ucsf.edu
Making Informed Food Choices
Learn how to read nutrition labels to make informed food choices. Understanding the information on the label empowers you to select healthier options. By paying attention to serving sizes, calories, and nutrient content, you can make better decisions for your overall well-being.
Reading Beyond The Front Label
Utilizing Nutrition Labels For Healthier Eating
Making informed food choices is crucial for maintaining a healthy lifestyle. By understanding how to read nutrition labels, you can ensure you are making the best choices for your body.
Reading Beyond The Front Label
When analyzing a product, always go beyond the front label. Check the nutrition label on the back for accurate information.
Utilizing Nutrition Labels For Healthier Eating
Use nutrition labels to make healthier choices. Look at serving sizes, calories, and % Daily Value to guide your decisions.
When reading nutrition labels, pay attention to the ingredients list. Focus on the first few ingredients, as they make up the majority of the product.
Check for items like added sugars and unhealthy fats. Avoid products with high amounts of these ingredients for better health.
Incorporate fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins in your diet. Choose products with higher percentage of essential nutrients.
Reading nutrition labels allows you to make informed decisions about the food you consume. Prioritize products that align with your health goals.

Credit: www.healthline.com
Frequently Asked Questions On How To Read Nutrition Labels
What Is The Easiest Way To Read Nutrition Labels?
The easiest way to read nutrition labels is by checking serving size first. Then look at calories, nutrients, and % Daily Value. Pay attention to ingredients and avoid items with added sugars and unhealthy fats. Compare similar products for better choices.
How Do You Read A Food Label With Carbs And Sugar?
To read a food label with carbs and sugar, check the total carbohydrates and sugars on the label. Consider portion size and the grams of sugar and carbs per serving. Remember to account for added sugars and opt for products with lower sugar and carb content.
How Do You Analyze Nutrition Labels?
To analyze nutrition labels, check serving size, total calories, and nutrient amounts. Look for added sugars, unhealthy fats, and high sodium levels. Compare with daily intake recommendations.
What Is The 5/20 Rule On Nutrition Labels?
The 5/20 rule on nutrition labels refers to a guideline for assessing the nutritional value of a food product. It suggests that if a nutrient, such as fat or sodium, is listed as 5% or less, it is considered low.
Conversely, if a nutrient is listed as 20% or more, it is considered high. This rule helps consumers make informed choices about their food intake.
Conclusion
Making educated food decisions requires knowing how to interpret nutrition labels. By analyzing the information provided, you can determine the nutritional value of a product and make healthier choices for yourself and your family. Remember to look for key elements such as serving size, calories, and percentages of daily values.
With this knowledge, you are empowered to prioritize your health and well-being. Don’t forget to read the labels and make better choices for a healthier future!


1 thought on “How to Read Nutrition Labels – Best Nutrition Facts”