Back knee pain location charts identify specific areas of discomfort behind the knee. These charts help diagnose the underlying causes.
Back knee pain can be a debilitating issue affecting daily activities. Pain may stem from various sources, including muscle strain, ligament injuries, or joint problems. Accurate diagnosis is crucial for effective treatment. A back knee pain location chart assists in pinpointing the exact area of discomfort, aiding healthcare providers in identifying the cause.
Understanding the pain’s origin helps in developing a tailored treatment plan. This targeted approach enhances recovery and reduces the risk of further injury. For anyone experiencing persistent back knee pain, consulting a specialist is essential for proper diagnosis and management.
Deciphering Back Knee Pain
Understanding back knee pain can be challenging. This guide will help you identify causes and symptoms.
Identifying Common Causes
- Arthritis: This affects the knee joints, causing pain and stiffness.
- Baker’s Cyst: A fluid-filled cyst behind the knee causing discomfort.
- Hamstring Injury: A hamstring muscle strain or tear.
- Tendonitis: Inflammation in the tendons around the knee.
Symptoms To Monitor
Pay attention to these symptoms:
- Swelling: Noticeable swelling behind the knee.
- Stiffness: Difficulty in bending or straightening the knee.
- Pain: Persistent pain during movement or rest.
- Weakness: Feeling of instability or weakness in the knee.
| Symptom | Possible Cause |
|---|---|
| Swelling | Baker’s Cyst |
| Stiffness | Arthritis |
| Pain | Tendonitis |
| Weakness | Hamstring Injury |
Anatomy Behind Knee Discomfort
Understanding knee pain helps you manage it better. The knee is complex. Knowing its parts helps identify pain sources. This section explores the knee’s anatomy.
The Structure Of The Knee Joint
The knee joint connects the thigh bone to the shin bone. It includes these parts:
- Femur (Thigh Bone): The top bone in your leg.
- Tibia (Shin Bone): The larger bone in your lower leg.
- Patella (Kneecap): The small bone in front of the knee.
These bones are held together by ligaments:
- Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL): Controls forward movement.
- Posterior Cruciate Ligament (PCL): Controls backward movement.
- Medial Collateral Ligament (MCL): Provides inner knee stability.
- Lateral Collateral Ligament (LCL): Provides outer knee stability.
Muscles And Tendons Involved
Muscles and tendons are crucial for knee function. The main muscles include:
- Quadriceps: Located at the front of the thigh. They help straighten the knee.
- Hamstrings: Located at the back of the thigh. They help bend the knee.
The key tendons involved are:
| Tendon | Function |
|---|---|
| Patellar Tendon | Connects the kneecap to the shin bone. |
| Quadriceps Tendon | Connects the quadriceps muscles to the kneecap. |
Knowing these structures helps identify where knee pain starts. This knowledge is the first step to relief.
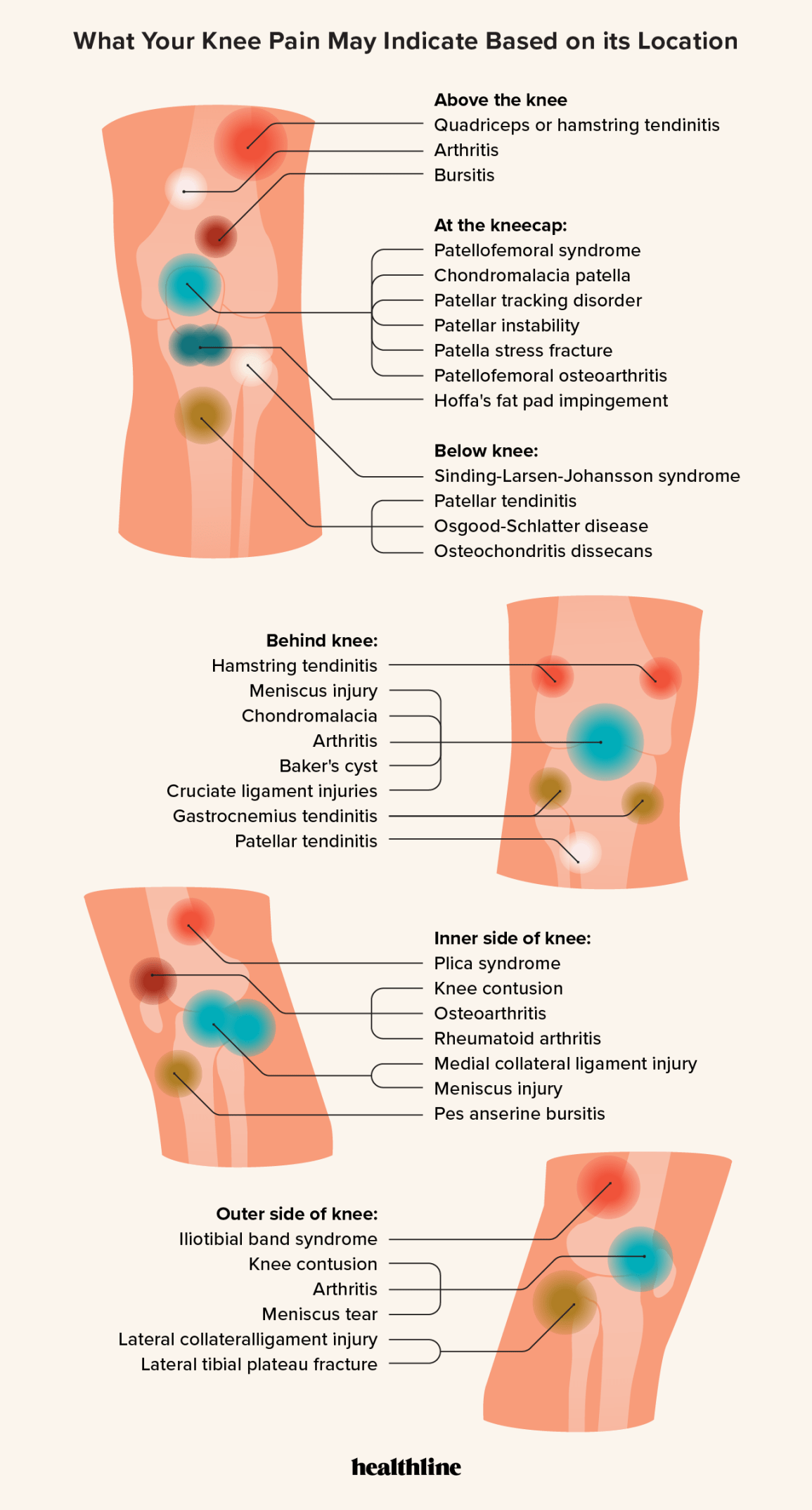
The Back Knee Pain Location Chart
The back knee pain location chart helps identify pain origins. This chart is a tool for understanding different pain areas. Knowing the exact pain spot can guide treatment. It helps doctors and patients communicate effectively.
Reading The Chart
Reading the chart is simple. Each section represents a specific area. Look at the chart and find your pain spot. The chart is divided into zones. Each zone shows a potential cause.
- Front of the knee
- Back of the knee
- Inside of the knee
- Outside of the knee
Match your pain to the chart. This will help you understand the cause. It can also indicate the severity of the pain.
Pain Points And What They Indicate
| Pain Point | Possible Cause |
|---|---|
| Front of the Knee | Patellar tendinitis, bursitis |
| Back of the Knee | Baker’s cyst, hamstring injury |
| Inside of the Knee | MCL injury, meniscus tear |
| Outside of the Knee | LCL injury, IT band syndrome |
Knowing these pain points helps in diagnosis. It guides the treatment plan. Always consult a doctor for severe pain.
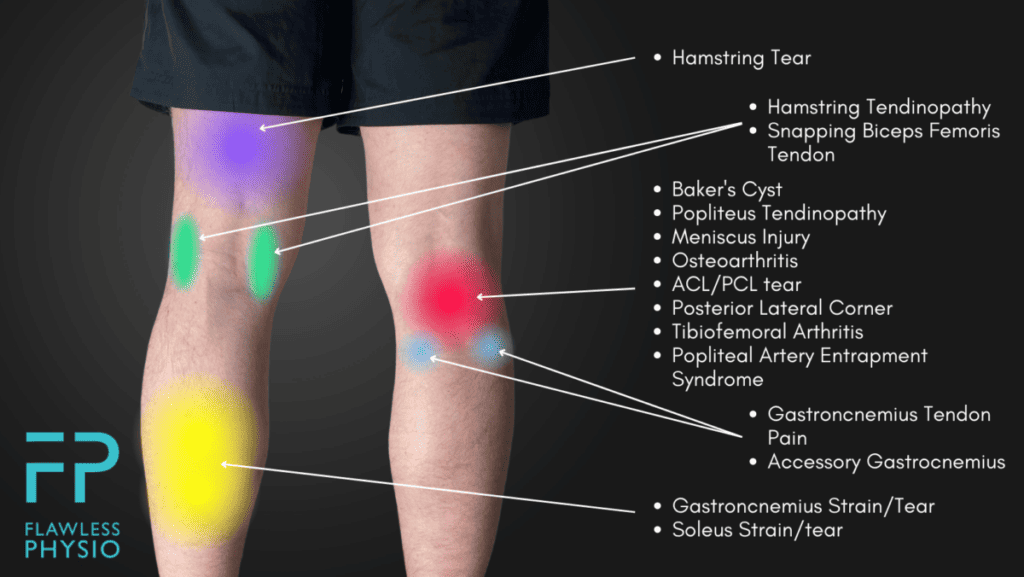
Credit: flawlessphysio.co.uk
Types Of Back Knee Pain
Understanding the types of back knee pain can help in managing it better. Pain in the back of the knee can vary in intensity and duration. This section covers the differences between acute and chronic pain and explains specific conditions that can cause this discomfort.
Acute Vs. Chronic Pain
Acute pain is sudden and sharp. It often results from an injury or accident. This type of pain usually lasts less than six weeks.
Chronic pain is long-lasting. It persists for more than three months. It may be due to an underlying condition or previous injury.
Specific Conditions Explained
Several conditions can cause pain in the back of the knee. Here are some common ones:
- Hamstring Strain: This occurs due to overstretching or tearing of the hamstring muscles.
- Baker’s Cyst: A fluid-filled cyst that causes swelling and pain.
- Meniscus Tear: This involves a tear in the cartilage of the knee.
- ACL Injury: The anterior cruciate ligament can be torn or sprained.
Comparison Table
| Condition | Symptoms | Duration |
|---|---|---|
| Hamstring Strain | Sharp pain, swelling | Acute |
| Baker’s Cyst | Swelling, tightness | Chronic |
| Meniscus Tear | Pain, stiffness | Acute/Chronic |
| ACL Injury | Severe pain, instability | Acute |
Diagnosing Back Knee Pain
Back knee pain can be challenging to diagnose due to its complex nature. Proper diagnosis is crucial to address the root cause effectively. This section explores the key aspects of diagnosing back knee pain.
When To Seek Medical Advice
Knowing when to seek medical advice is essential. Care must be given to persistent pain that lasts more than a few days. Consult a doctor if the pain is severe or accompanied by swelling. Seek help if you experience limited mobility or a noticeable deformity.
- Persistent pain lasting more than a few days
- Severe pain or swelling
- Limited mobility or deformity
Tests And Imaging Techniques
Doctors use various tests and imaging techniques to diagnose back knee pain accurately. Physical examinations help determine pain locations and movements that cause discomfort.
Below is a table summarizing common tests and imaging methods:
| Test/Technique | Description |
|---|---|
| X-ray | Identifies bone fractures and alignment issues. |
| MRI | Provides detailed images of soft tissues and cartilage. |
| Ultrasound | Examines tendons, ligaments, and muscles. |
| CT Scan | Offers cross-sectional images for a comprehensive view. |
Doctors may also recommend blood tests to rule out infections or arthritis. Joint aspiration may be performed to analyze fluid from the knee joint.
- Physical examination
- X-ray
- MRI
- Ultrasound
- CT Scan
- Blood tests
- Joint aspiration
Home Remedies For Immediate Relief
Back knee pain can be bothersome. Thankfully, there are simple home remedies. These remedies offer immediate relief and can be done easily.
Ice Vs. Heat Therapy
Ice therapy can reduce swelling and numb the pain. Apply an ice pack to the back of the knee for 15-20 minutes. Repeat this every 2-3 hours during the first 48 hours.
Heat therapy helps to relax and loosen tissues. Additionally, it increases localized blood flow. Spend fifteen to twenty minutes using a heated pad or towel. Ensure you do this after the initial 48 hours of injury.
Exercises And Stretches
Specific exercises and stretches can ease back knee pain. These can strengthen muscles and improve flexibility.
- Hamstring Stretch: Sit on the floor with legs straight. Hold onto your toes for a duration of 15 to 30 seconds.
- Quadriceps Stretch: Stand on one leg. Pull the other foot towards your buttock. Hold for 15-30 seconds.
- Calf Stretch: Stand facing a wall. Place one foot behind the other. While maintaining a straight back leg, bend the front knee. Hold for 15-30 seconds.
Repeat these stretches 3-4 times daily for best results.
Medical Treatments And Interventions
Experiencing back knee pain can significantly disrupt daily activities. Understanding the available medical treatments and interventions is crucial. This section explores different approaches to alleviate pain and improve mobility.
Medication Options
Medications can offer significant relief from back knee pain. Here are some common options:
- Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs): Help reduce pain and inflammation.
- Acetaminophen: Provides pain relief without reducing inflammation.
- Topical Analgesics: Creams or gels applied to the skin for localized relief.
- Muscle Relaxants: Useful for muscle spasms and tightness.
- Corticosteroid Injections: Offer powerful anti-inflammatory effects directly at the pain site.
Surgical Procedures
Surgery might be necessary for severe or persistent back knee pain. Here are some surgical options:
| Procedure | Description |
|---|---|
| Arthroscopy | Minimally invasive, uses small instruments to repair knee damage. |
| Knee Replacement | Removes damaged parts, replaces them with artificial components. |
| Osteotomy | Realigns bones to reduce pressure on the knee joint. |
| Synovectomy | Removes inflamed synovial tissue causing pain. |
Each surgical procedure comes with its risks and benefits. In order to make an informed choice, go over these with your physician.

Credit: www.towncenterortho.com
Preventing Back Knee Pain
Preventing back knee pain is essential for maintaining mobility and comfort. By adopting proactive measures, you can avoid discomfort and enhance your overall well-being. This section explores key strategies for preventing back knee pain through lifestyle adjustments and the use of protective gear.
Lifestyle Adjustments
Simple lifestyle changes can greatly reduce back knee pain. Sustain a healthy weight to relieve knee strain. Regular exercise strengthens muscles and supports the knee joint. Give priority to low-impact exercises like walking, cycling, and swimming.
Proper posture is vital. Stand and sit straight to align your spine. Use ergonomic furniture to support your back and knees. When sitting or standing for extended amounts of time, take breaks. To maintain the flexibility of your joints, move and stretch.
Protective Gear And Best Practices
Wearing the right gear can prevent injuries and back knee pain. Use knee braces or supports during physical activities. Choose shoes with good cushioning and support. This reduces impact and supports your knees.
Practice proper techniques while lifting heavy objects. Bend your knees and keep your back straight. Avoid twisting your body. To get your muscles and joints ready for exercise, warm up first.
Here is a table summarizing key protective gear and best practices:
| Protective Gear | Best Practices |
|---|---|
| Knee Braces | Use during physical activities |
| Supportive Shoes | Choose with good cushioning |
| Ergonomic Furniture | Support back and knees |
| Proper Lifting Techniques | Bend knees, keep back straight |
By following these guidelines, you can significantly reduce the risk of back knee pain. Stay active, use the right gear, and maintain good posture. Your knees will thank you!
Navigating Chronic Pain Management
Chronic back knee pain can be debilitating. Managing it requires a thoughtful approach. Understanding pain location charts helps. Let’s explore strategies for managing chronic pain effectively.
Long-term Strategies
Developing long-term strategies for chronic pain involves several steps. Consistency is key. Here are some approaches:
- Exercise Regularly: Gentle exercises help strengthen muscles.
- Maintain a Healthy Diet: Overall health is supported by proper nutrition.
- Physical Therapy: Regular sessions improve mobility.
These strategies reduce pain over time. For optimal effects, incorporate them into your everyday schedule.
Support And Resources
Having access to support and resources is vital. Here are some helpful resources:
| Resource | Description |
|---|---|
| Support Groups | Connect with others experiencing similar pain. |
| Online Forums | Share experiences and tips. |
| Medical Professionals | Get professional advice and treatment plans. |
Utilize these resources for better pain management. They offer support and guidance.
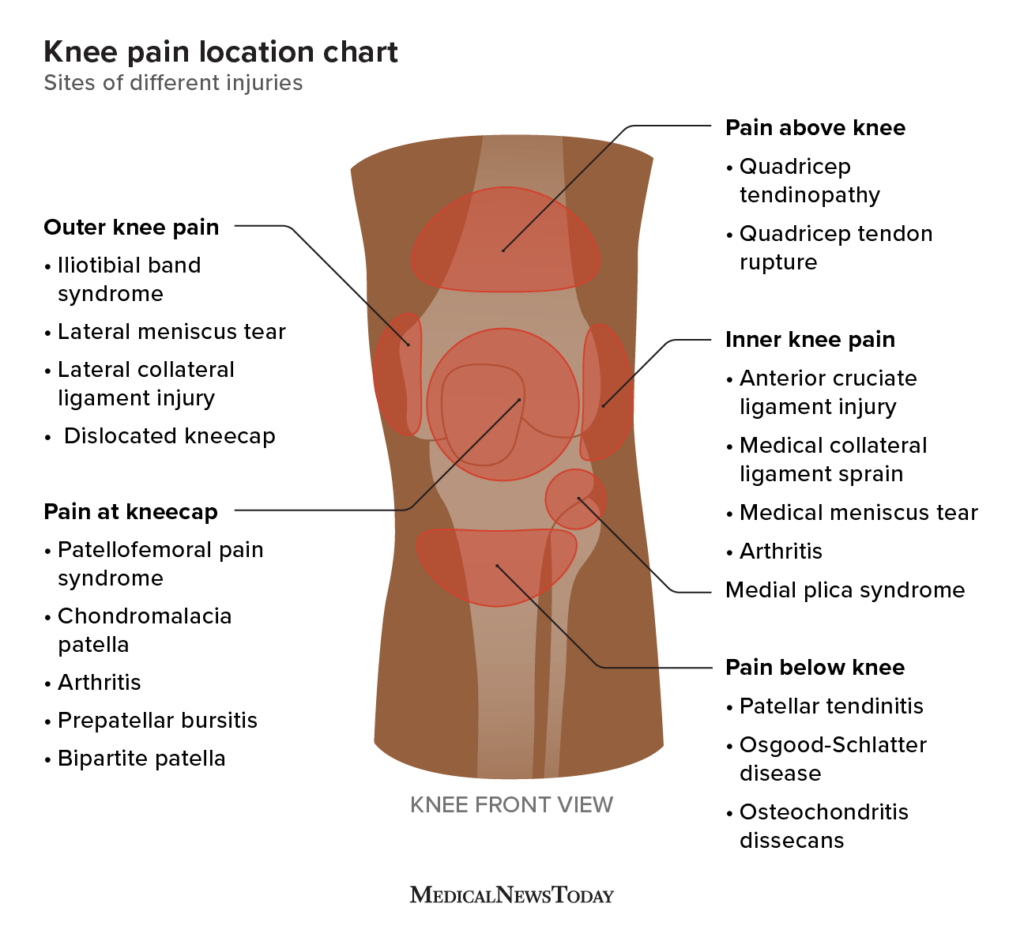
Credit: www.medicalnewstoday.com
Frequently Asked Questions
What Does It Mean When The Back Of Your Leg Hurts Behind The Knee?
Pain behind the knee could indicate a hamstring injury, Baker’s cyst, or tendonitis. It might also suggest deep vein thrombosis. Consult a doctor for a proper diagnosis.
What Does A Pulled Tendon Behind The Knee Feel Like?
A pulled tendon behind the knee feels like sharp pain, stiffness, and swelling. You may also experience difficulty in bending the knee.
How Do I Know If My Knee Pain Is Coming From My Back?
Knee pain from your back often includes symptoms like tingling, numbness, or radiating pain down the leg. Consult a doctor for diagnosis.
How To Describe Knee Pain Location?
Describe the knee pain location by pinpointing the exact area. Specify whether it’s front, back, inside, or outside. Mention any specific spots, like the kneecap or joint.
Conclusion
Understanding the back knee pain location chart can guide effective treatment. Recognize specific pain points to address issues accurately. This chart simplifies identifying pain sources, ensuring better care. Use it as a tool for improved knee health and pain management.
Prioritize your knee health for a more active and pain-free life.
<script type="application/ld+json">
{
"@context": "https://schema.org",
"@type": "Article",
"mainEntityOfPage": {
"@type": "WebPage",
"@id": "https://yoursoulhealth.com/back-knee-pain-location-chart/"
},
"headline": "Back Knee Pain Location Chart: Your Guide to Relief",
"description": "Back knee pain location charts identify specific areas of discomfort behind the knee. These charts help diagnose the underlying causes.",
"image": "https://yoursoulhealth.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/07/back-knee-pain-location-chart-551x1024.png",
"author": {
"@type": "Person",
"name": "Tanshir Bhuiyan",
"url": "https://yoursoulhealth.com/author/admin/"
},
"publisher": {
"@type": "Organization",
"name": "YourSoulHealth",
"logo": {
"@type": "ImageObject",
"url": "https://yoursoulhealth.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/05/Soul-Health-Without-bg.png"
}
},
"datePublished": "2024-09-06"
}
</script>
I am a health writer and blogger based in the US and UK. I have been with the health department for six years. And I give advice on various health problems and solutions. I have a lot of experience in health matters and I share it here.